Drainage Water Management (DWM), given sufficient rainfall, allows the user
to manage their water by raising and lowering their outlet depth.
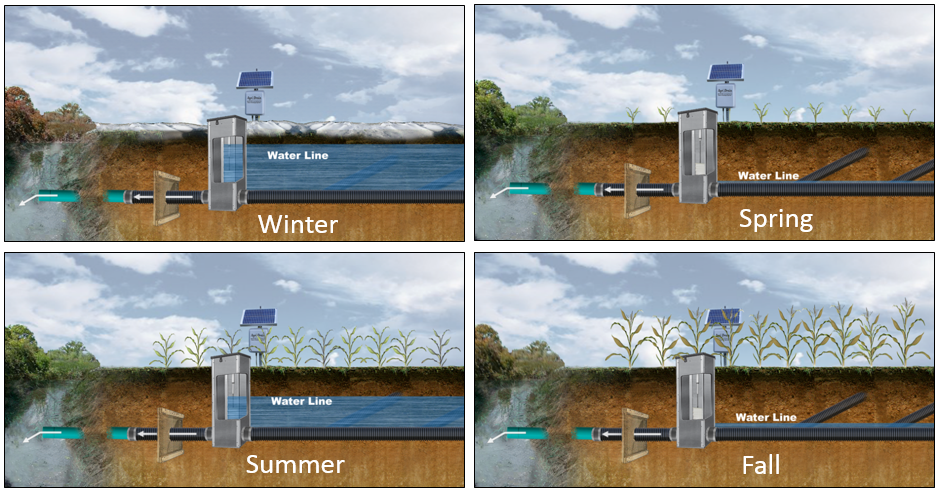
Drainage Water Management (DWM) is a low cost, effective water conservation practice that controls soil water table elevations and the timing of water discharges from subsurface agricultural drainage systems. DWM simultaneously improves water quality and the soil environment for better crop yields. This conservation practice enables land with limited productivity due to wetness to become more productive and more profitable when implemented with existing or new tile drainage systems. Drainage water management allows users to manage their water table when structures for water control are installed in a main, sub-main, or lateral in the tile system. By using this drainage water management system in place of conventional drainage, producers conserve water, and can reduce nutrient losses to streams by 30-50%.
With drainage water management, installed water control structures are adjusted based on the season and drainage needs throughout the year. The DWM system management includes raising the water level after harvest to hold as much water as possible in the soil profile. This facilitates as much denitrification as possible in the offseason to gain environmental benefits. In the spring, the water table is lowered to facilitate field work and planting. Once field work is completed, water levels are raised and then managed at the proper level to conserve as much water for crop use as possible while not damaging crop root development.
“The effect of controlled drainage on crop yields was strongly dependent on management.
Average response was a potential 10% increase in yields when controlled drainage is effectively managed.”
–R. Wayne Skaggs, North Carolina State University
Phone: (800) 232-4742 or Email: andy@ecoexch.com